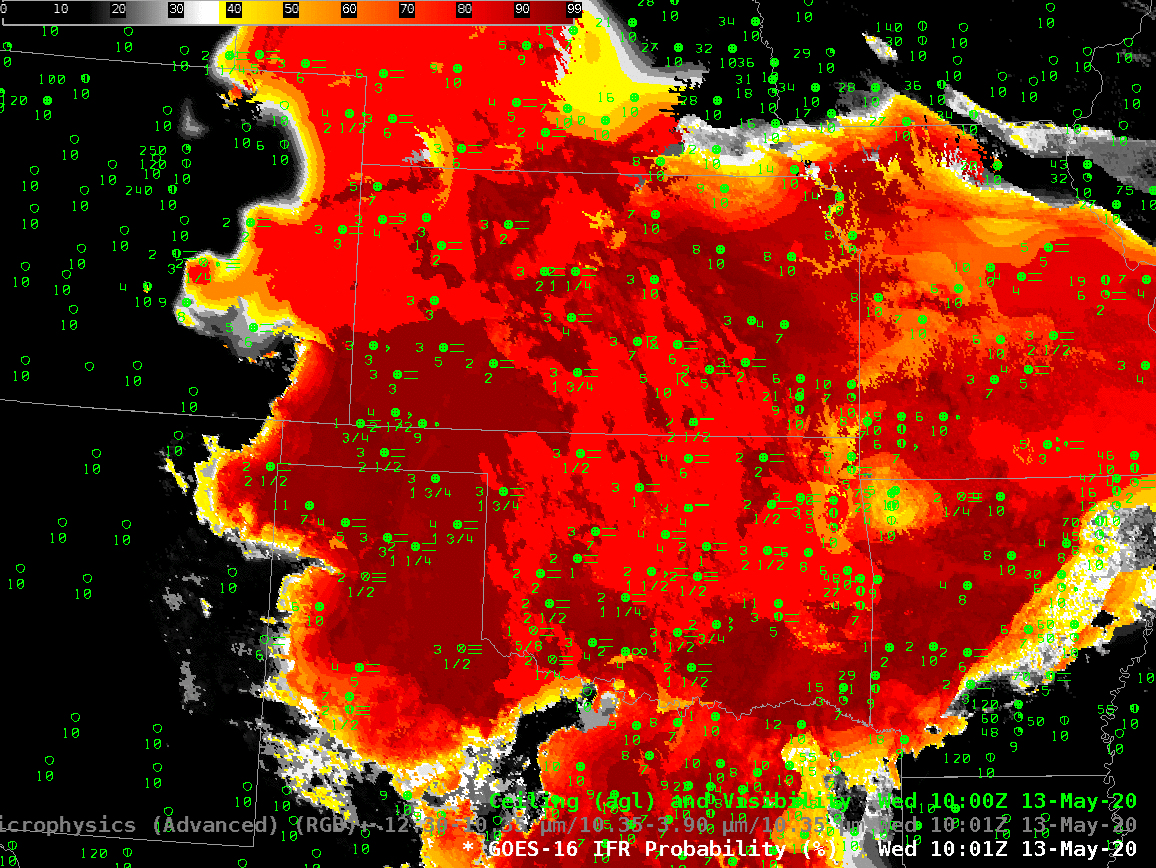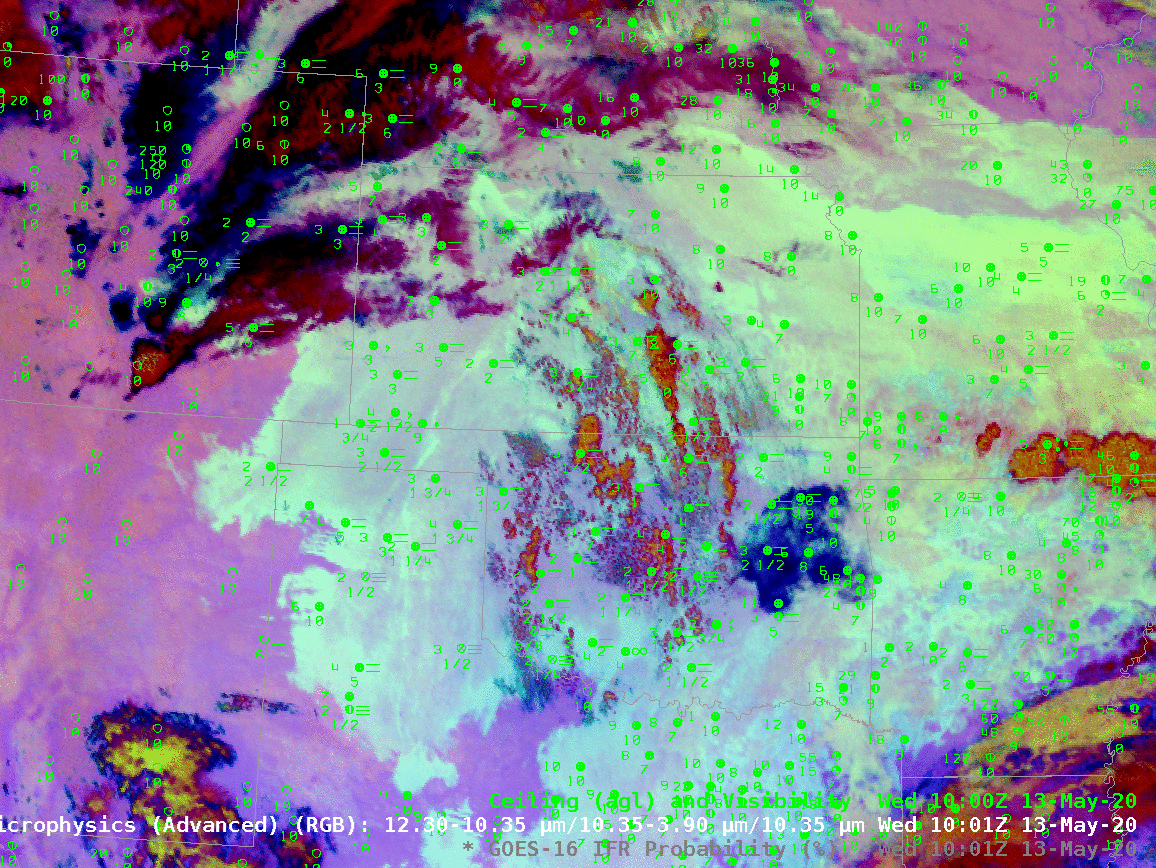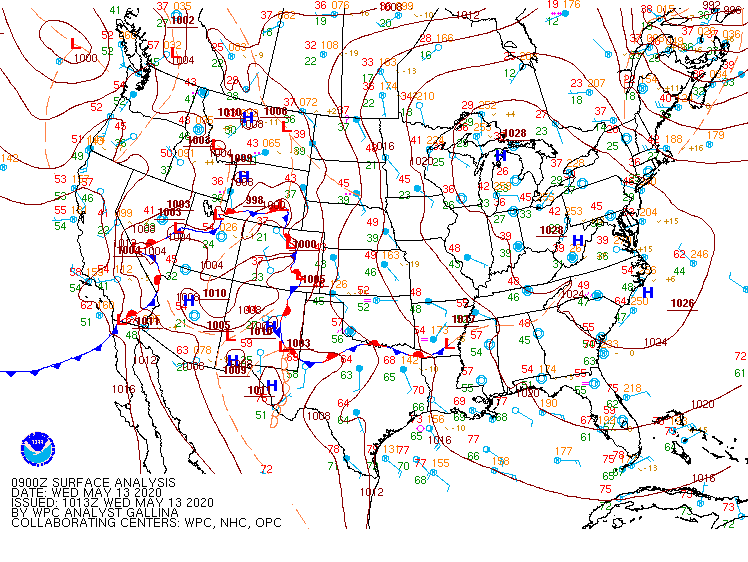
Much of the central Plains of the United States was under easterly flow during the night on 12-13 May 2020, as suggested by the surface analysis above. Strong High Pressure over the Great Lakes and lower pressures over the Rocky Mountains drove that upslope flow. Consequently, IFR conditions were common over much of the Plains, as shown below.
The animation, below, of IFR Probability (overlain with surface observations and ceilings and visibilities) shows high probabilities. There is good correlation between regions with High IFR Probabilities — red and orange — and regions with low ceilings and reduced visibilities. The highest probabilities, dark red in the enhancement, occur where satellite data shows low clouds and where model data shows low-level saturation. Note that there is a trend towards less satellite information in the IFR Probability field with time over central Oklahoma and south-central Kansas because of developing convection.
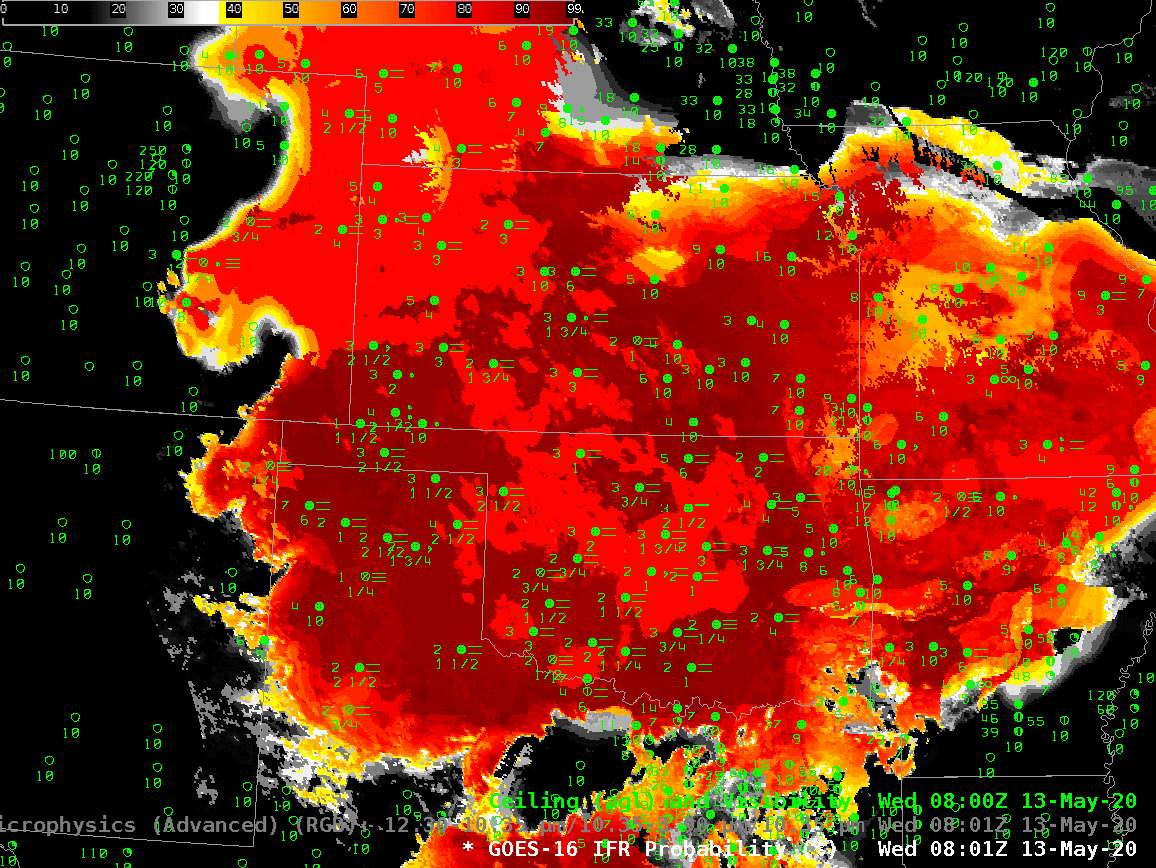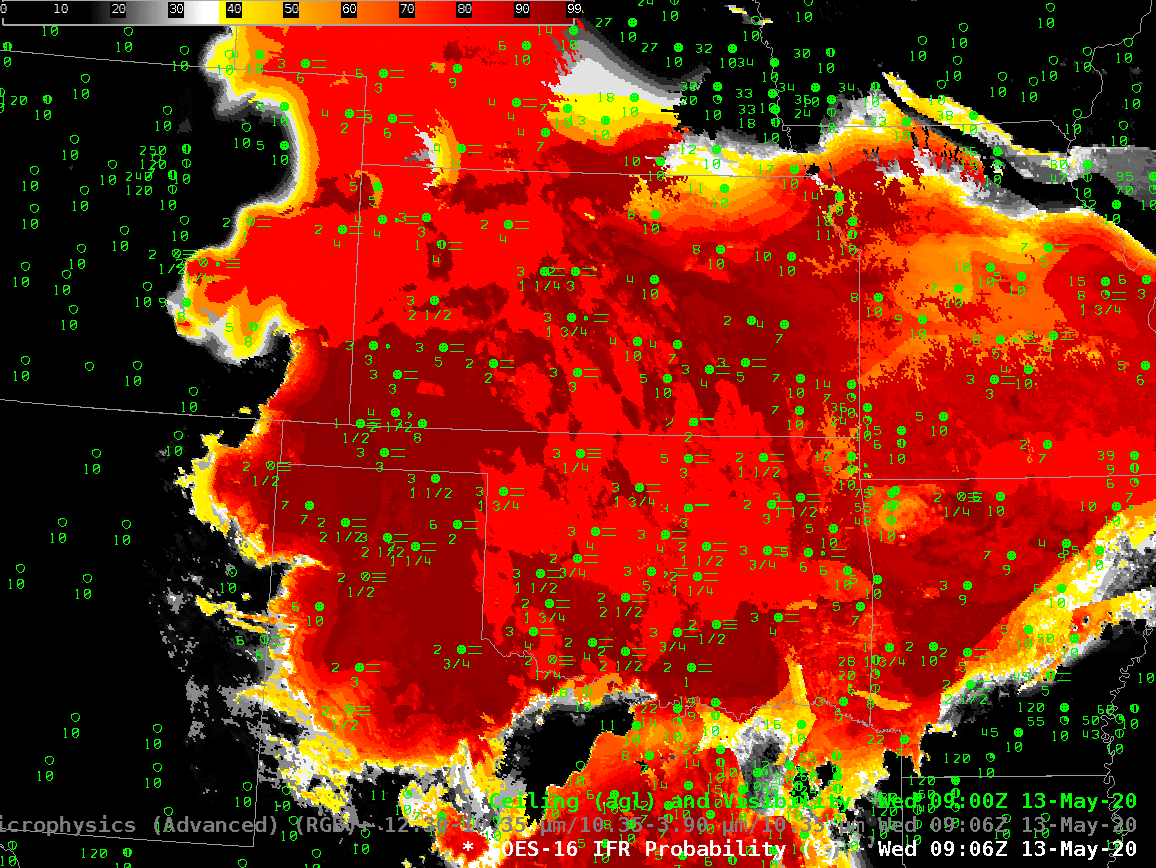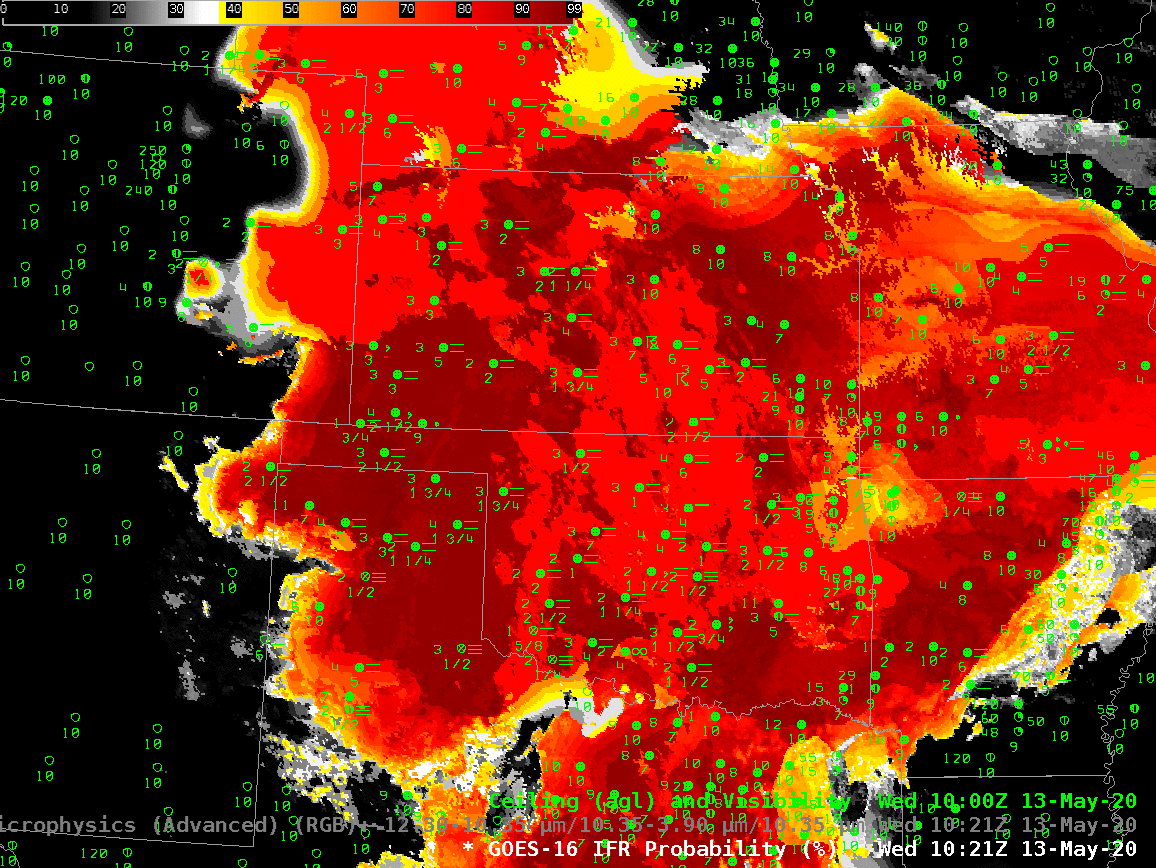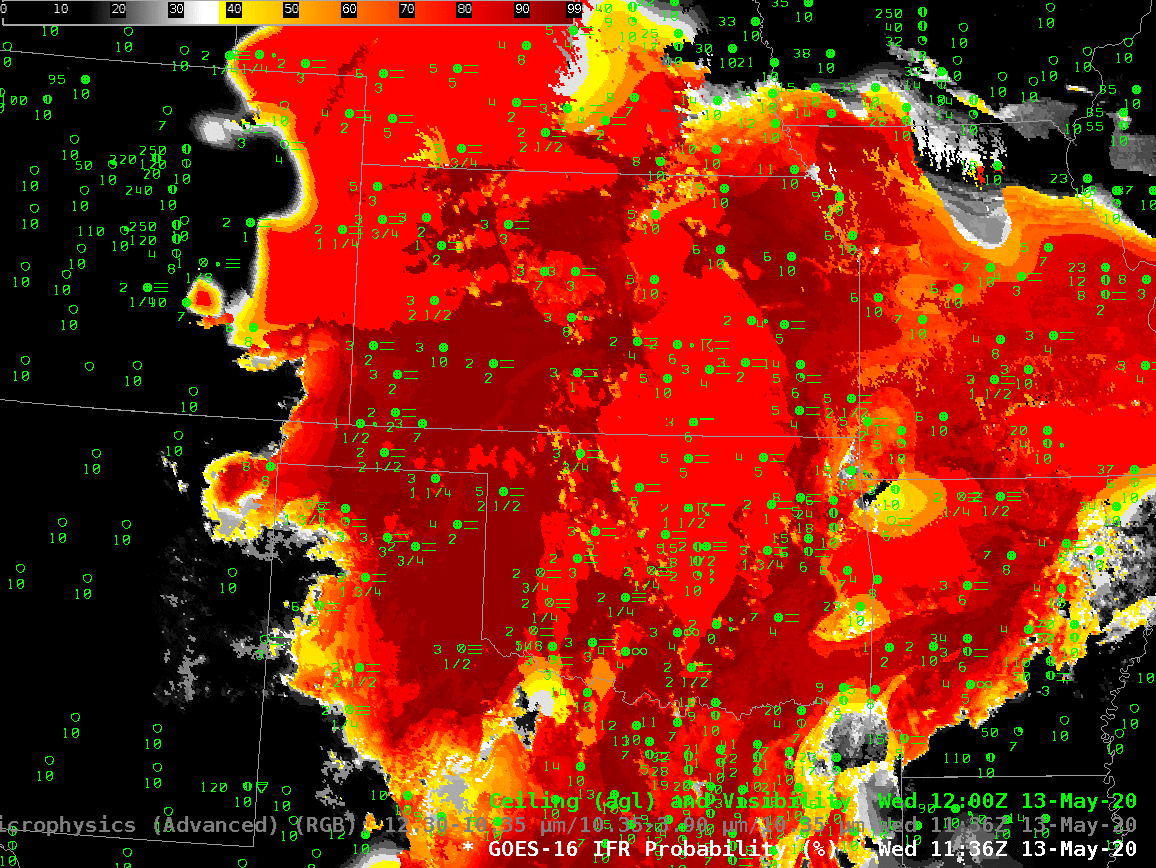
The night time microphysics RGB, shown below, is also used to detect regions of low clouds; they typically appear yellowish at this time of year. The challenge with the RGB use in highlighting IFR conditions is two-fold: high clouds will mask the low cloud signal (as in the case of developing convection over Oklahoma, or with cirrus over Colorado and Nebraska). The RGB can also struggle to differentiate between fog and low stratus. Note also in this animation how the effect of the rising sun becomes apparent at the end of the animation over the eastern third of the image.
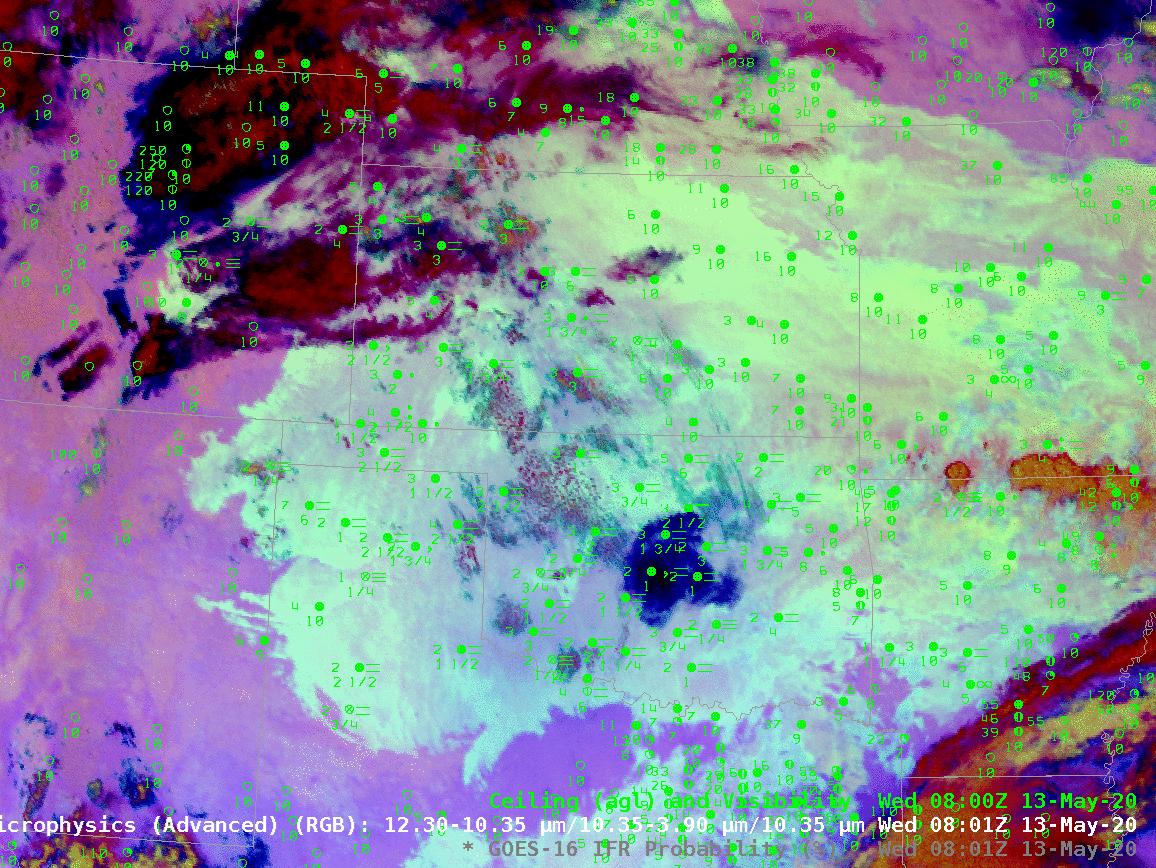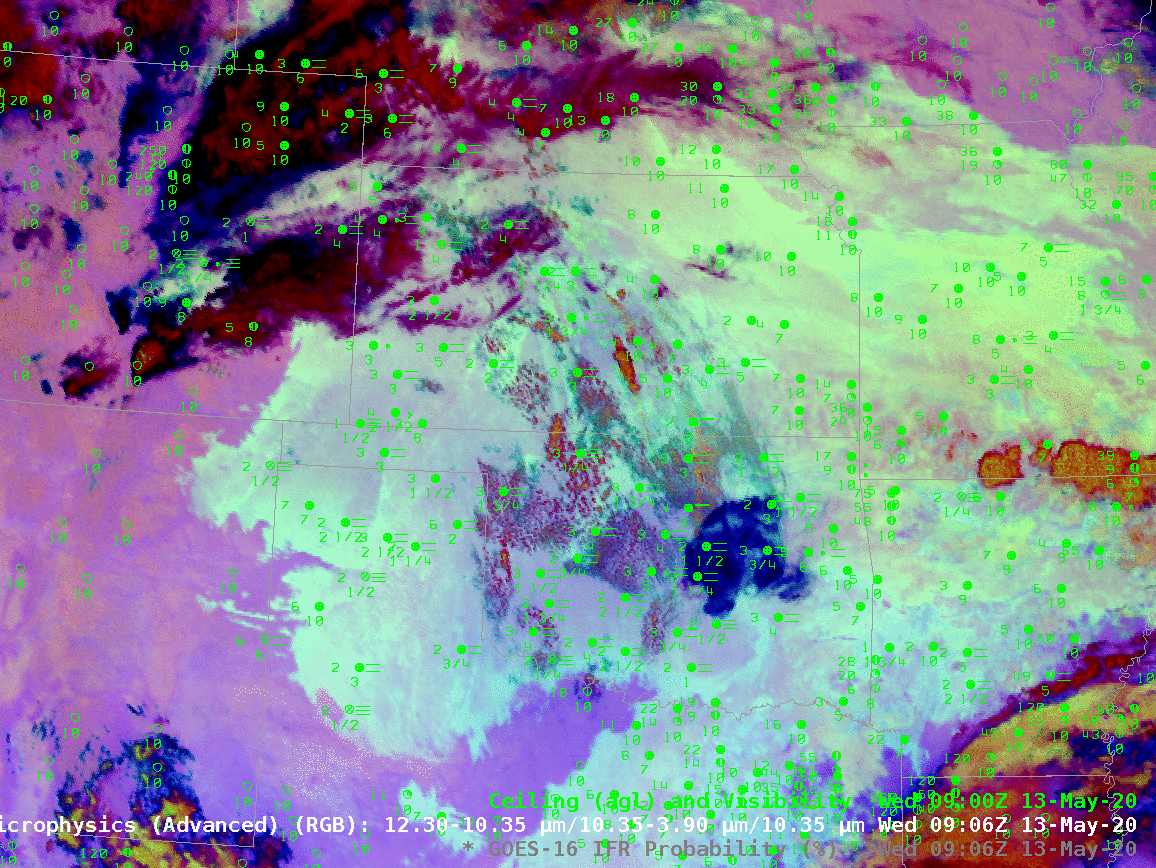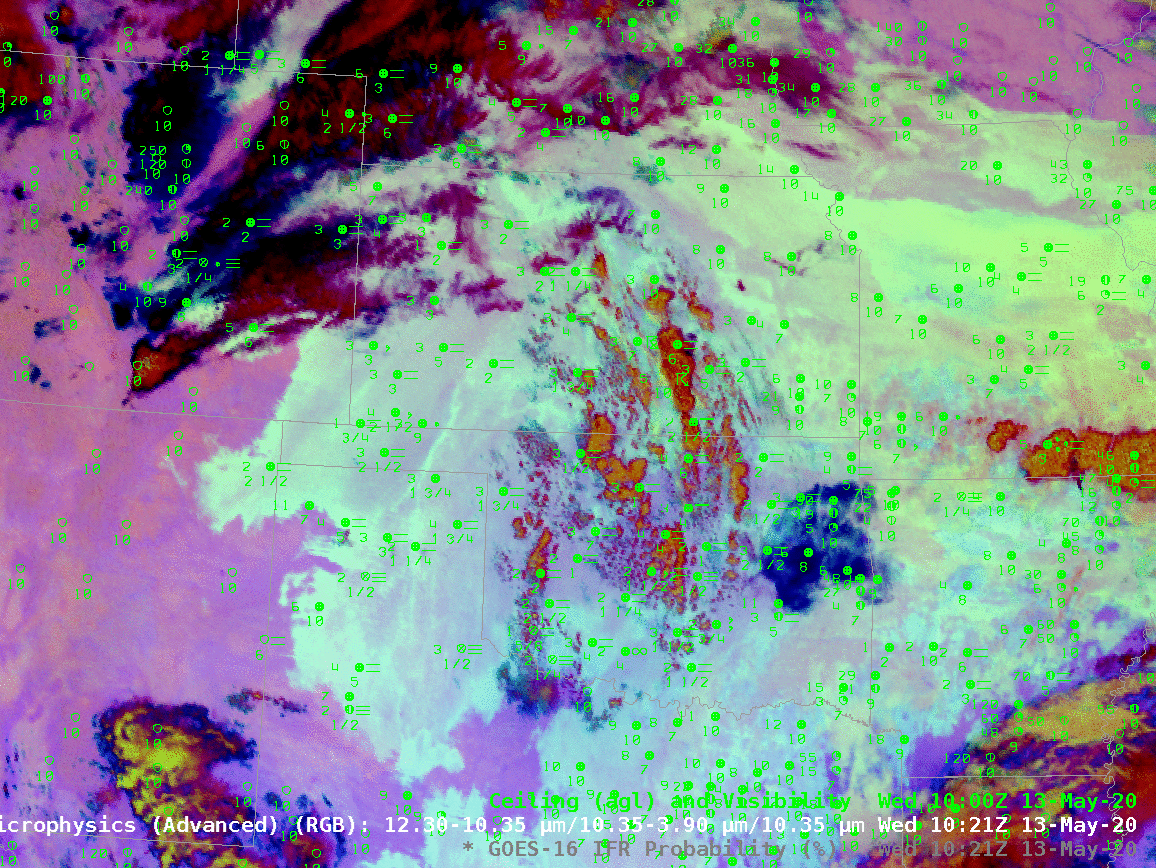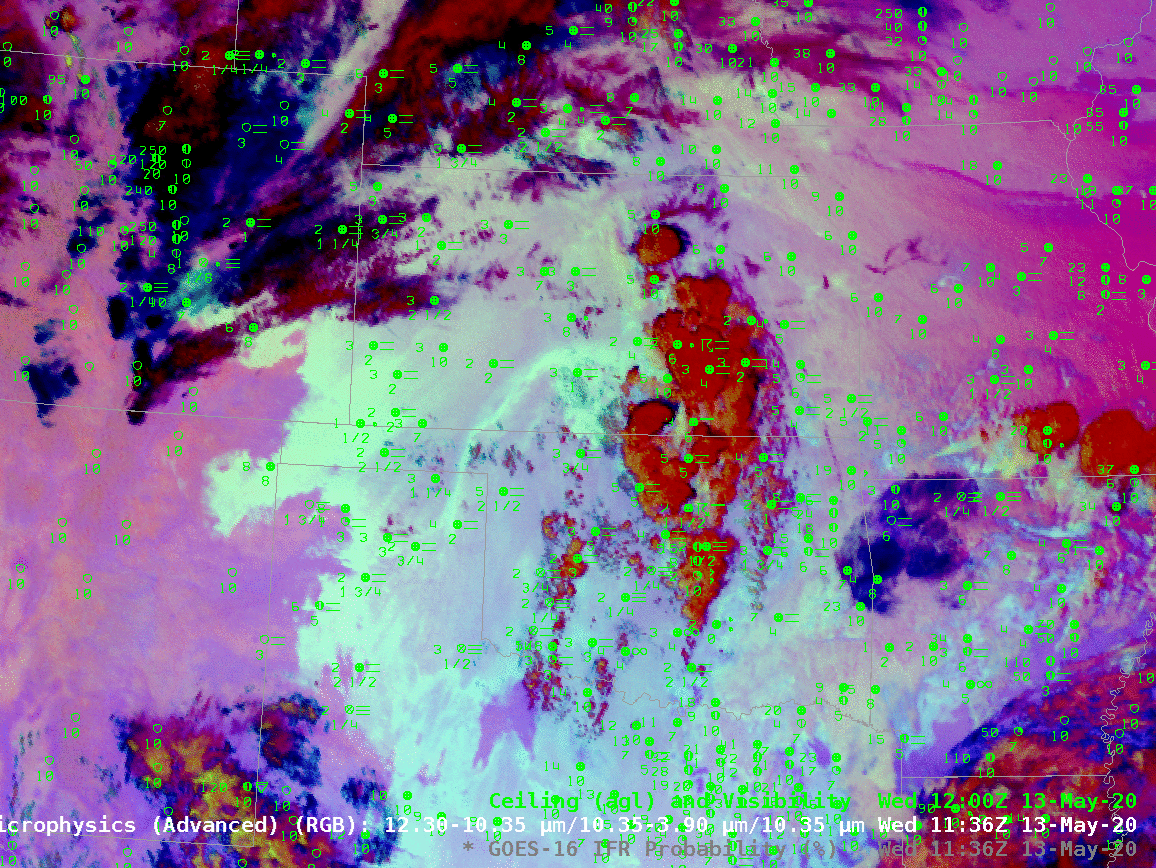
In the toggle below, the signal of low clouds in the RGB, yellow/cyan over the Texas panhandle (for example) has an echo in the IFR Probability field. In the absence of high clouds, both products will show regions of low clouds. The Night Time Microphysics RGB gives extra information about the cloud type in regions where high clouds are blocking the satellite view of low clouds (the purple region over Colorado/Nebraska and the reddish regions over Kansas and Oklahoma). In contrast, the IFR Probabilty field in those regions gives no information on the character of the higher cloud; the IFR Probability field in those regions is flat (i.e., not pixelated), the hallmark of IFR Probability that is derived chiefly from model fields, so all an analyst can tell is that a high cloud is present.